About Upper Back Pain

Upper back pain and middle back pain occurs from the base of the neck area to about the bottom of the rib area.
The ribs are attached in the front center of your chest to a long, flat bone called your sternum. From there, they wrap around your body to your back. Upper back pain is sometimes caused by a nerve in this area that is irritated, injures or pinched. The pain of a pinched nerve can also travel or radiate to other places, like your legs, arms, belly or chest.
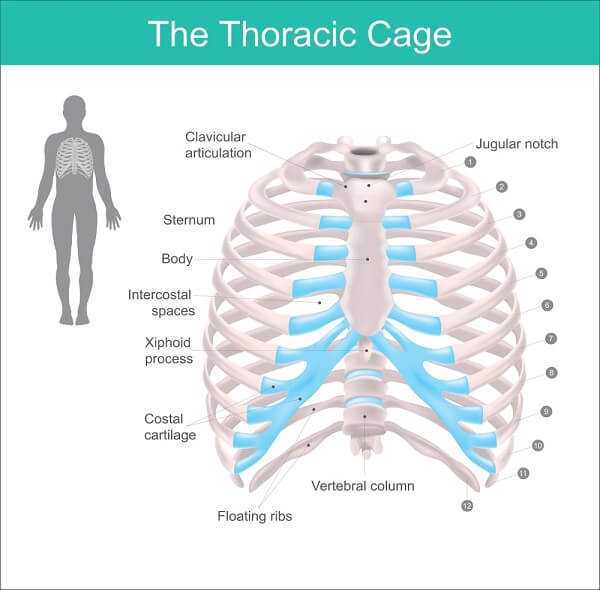
The middle and upper back is called the thoracic spine. It has several components, any of which can be the source of upper back pain:
- 12 bones called vertebrae that attach to your ribs. These vertebrae make up the longest segment of your spine.
- Disc between each vertebrae. These separate the vertebrae and act as shock absorbers when you move and walk
- Ligaments and muscles to hold your spine together
Prevalence
Upper back pain and pain in the middle back do not occur as commonly as pain in the lower part of the back. This is because the vertebrae in these parts of the spine are not as mobile as the bones in the neck or the lower back. They work instead to keep your back in position and help to protect your lungs and heart.
- Research has shown a higher prevalence of upper back pain in adolescents and children, especially in girls.
- It has been associated with the use of backpacks, participation is certain sports, difficulty with homework and the height of chairs used at school. Other risk factors for upper back pain include age transition of girls from early into late adolescence and impaired mental health.
Click “Back Packs and Back Pain” for more info.

Symptoms
Typical symptoms of upper back pain and pain in the middle back include:
- A Sharp, burning or dull pain
- Stiffness or tightness in the muscles
- Weakness in your legs or arms
- Loss of sensation, or numbness or tingling sensations in your legs, arms, belly or chest
- Inability to control your bowels or bladder
Causes
Upper back pain can be the result of a sudden injury or trauma. It can also occur due to muscle strain or be the result of poor posture that comes on gradually over a period of time.
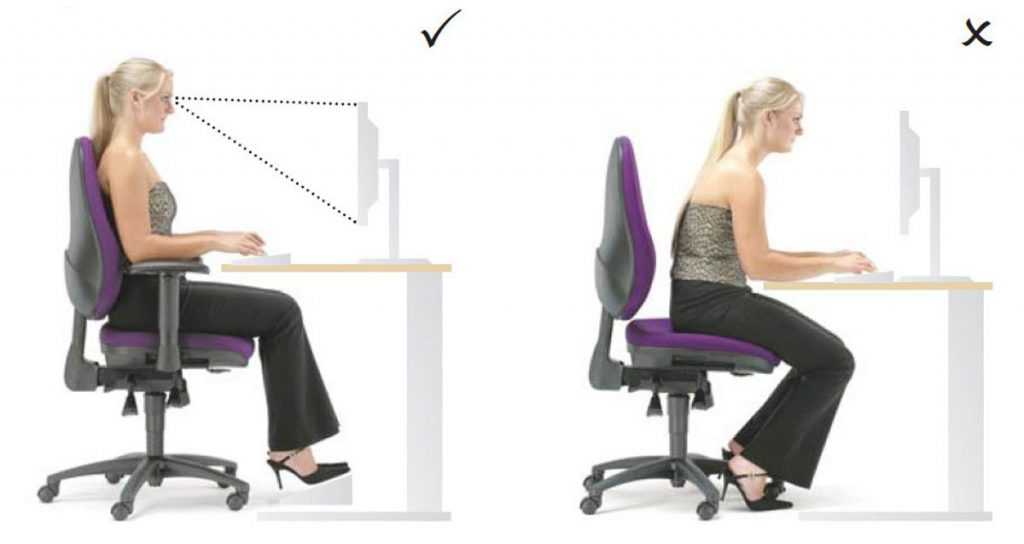

Recently, upper back pain has become a frequent symptom of people who spend much of their day working at a computer. It often occurs along with pain in the shoulders and/or the neck.
Muscle Irritation that Causes Upper Back Pain
Large muscles attach the shoulder girdle to the shoulder blade and to the back of the ribs in the upper back area. These large muscles of the upper back can easily become irritated, causing upper back pain known as myofascial pain. Muscle irritation and upper back pain can be caused by injuries related to overuse, such as repetitive movement or by de-conditioning. Muscular irritation can also be the result of sports injuries, motor vehicle accidents or muscle strains. If one particular area is extremely tender, the cause of upper back pain might be an active trigger point.
Joint Dysfunction that Causes Upper Back Pain
The ribs are connected to the spine by joints. If these joints become damaged or dysfunctional, upper back pain can result. Dysfunction in the joints is known as osteoarthritis. It occurs when cartilage that serves as a cushion for the joints in the spine wears down. Without this cushion, the bones rub against each other, resulting in damage and pain. Upper back pain caused by osteoarthritis is due to wear and tear damage of cartilage due to aging.
Click here to know more about Osteoarthritis.
Abnormal Curvatures that Cause Upper Back Pain
When the normal curves of the spine become exaggerated, upper back pain can result. The normal spine has a gentle S-shaped curve to help absorb shock and provide stability. When scoliosis develops, the spine develops an abnormal lateral curvature and may twist. In kyphosis, the upper spine becomes rounded and humped. Either of these conditions can cause upper back pain and severe curvatures can cause difficulty breathing.
For more information about this, click “All About Scoliosis“.
Uncommon Causes of Upper Back Pain
Conditions like spinal stenosis, disc herniations, degenerative disc disease and spinal instability (spondylolisthesis) are uncommon as causes of upper back pain. This is due to the fact that the upper back is very stable and has very little movement. Most herniated discs occur in the lower area (lumbar) of the spine where a lot of movement occurs.
In rare cases, upper back pain results due to thoracic disc disease. Significant trauma or injury can also result in a fracture of one of the thoracic vertebrae.
Diagnosis
To diagnose your upper back pain, your doctor will want to know about your symptoms, your past health history, and about your physical activities and work. You will be given a physical examination and your doctor might order imaging testing to determine if a herniated disc or a broken bone is causing your upper back pain.
The tests your doctor might order may include:
- X-rays: to see if there are any diseases or injuries present in your bones that might be contributing to your pain
- An MRI: to see if there are any diseases or injuries presentthat are affecting the nerves and discs of your spine and are causing upper back pain. These could include pinched nerves, herniated discs or tumors. An MRI can also show narrowing in the spinal canal.
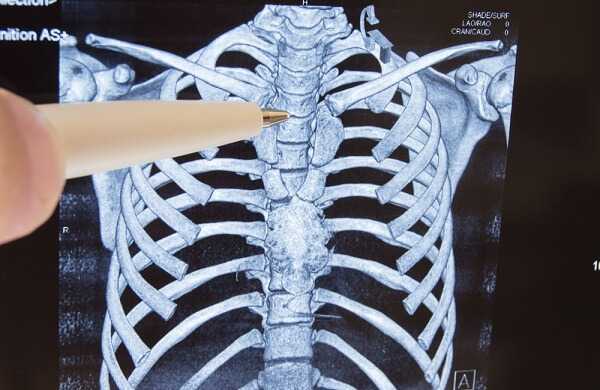
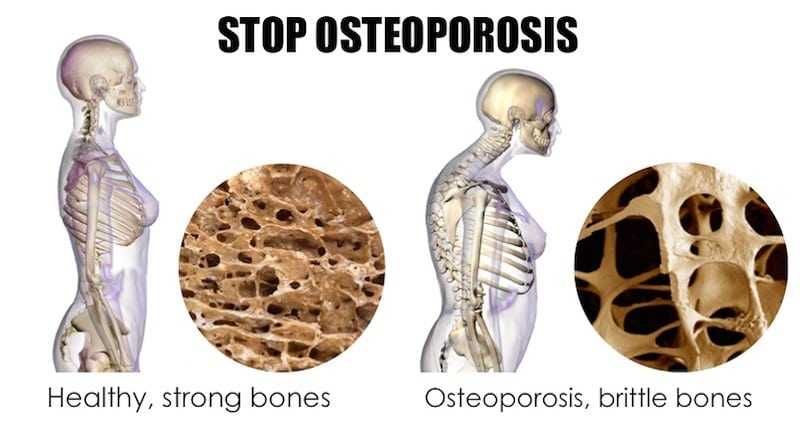
- A CT scan: to see if there are any fractures, tumors, narrowing of the spinal canal, herniated discs or infections. A CT scan will also show if osteoporosis has caused a compression fracture and if this is the reason for your upper back pain.
- A bone scan: to see if there is bone damage, an infection or a tumor. Doctors often use a bone scan to look for the cause of unexplained upper back pain.
- A nerve conduction study and electromyogram: to see how the nerve roots, muscles, and nerves that control your legs and arms are functioning. These tests can help find the source of upper back pain and pinpoint the reason for numbness, weakness and pain in the upper and lower extremities.
Non-surgical Treatment
In many cases of upper back pain, symptoms can be managed with conservative treatments like:
- Over-the-counter (OTC) pain relievers: These include medications such as acetaminophen and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) to relieve your pain. If OTC medications are not effective, your physician may give you a prescription for a stronger medication to relieve your upper back pain.
- Applications of ice or heat: to reduce stiffness and pain.
- Gentle stretches and exercises: to help strengthen and stretch the muscles in your shoulders, back and abdomen
- Physical therapy: to increase your balance, strength, and flexibility
- Massage: to relieve upper back pain, improve circulation and relieve muscle tension
- Manipulation of the spine: to improve function and reduce pain
- Acupuncture: as a form of alternative therapy for upper back pain

- Stronger prescription medications, such as narcotics to manage your upper back pain
- Muscle relaxants to relieve muscle tension and increase mobility
- Antidepressants to treat chronic upper back pain
- Steroid injections to relieve swelling and reduce pressure on irritated nerves. There is little proof to indicate these are effective in controlling upper back pain
- In some cases, your doctor may recommend wearing a back brace for support following a spinal fracture
Surgical Treatment
Surgery is seldom used to treat upper and middle back pain. If your doctor recommends surgery, the type will depend on the problem you have. Surgery choices may include:
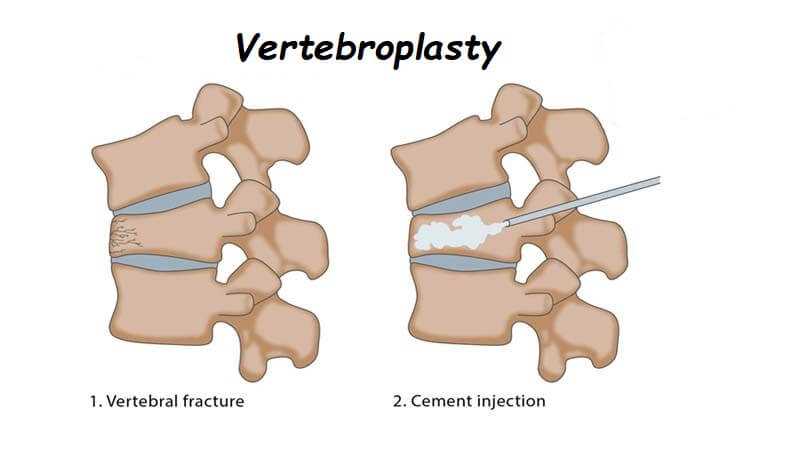
- Kyphoplasty or vertebroplasty: In these procedures, special bone-like cement is injected into the spine through a needle to try to stabilize a fractured vertebra. These operations are not performed often because fractures of the vertebrae usually heal without surgical treatment. There is no evidence that these surgeries are more effective than non-surgical treatment in treating upper back pain.
- In this procedure, the part of the disc that is bulging into the spinal canal is removed. Most discs that rupture in the upper back are not large enough to need surgery, but if your upper back pain is caused by a large herniation that is pressing on a spinal nerve, surgery may be necessary.
- Spinal decompression for stenosis: This procedure is done to widen a narrowed spinal canal to relieve pressure on spinal nerves or on the spinal cord that is causing upper back pain. Spinal stenosis in the upper back is uncommon, so this operation is not often performed on the upper back.
Prevention
- Exercise: One of the best ways to prevent upper back pain is to exercise. Consult with your doctor to find out which exercises will be best for you to strengthen and stretch the muscles in your shoulders, stomach and back. When your muscles are strong, they help support your balance, improve posture and reduce your chance of injury. Exercise and stretching can also help decrease upper back pain.
- Reduce your stress: Try methods like progressive relaxation exercises, deep breathing or meditation to manage stress and muscle tension and prevent episodes of upper back pain.
- Eat healthy foods: Manage your risk of compression fractures and upper back pain by making sure your diet contains adequate amounts of vitamin D and calcium.
- Stop smoking: And if you don’t smoke, avoid second-hand smoke. Smoking decreases circulation and inhibits healing.
- Learn how to lift: Never lift with your back, use your leg muscles. Know your limits and avoid upper back pain due to injury by getting help with heavy loads.
- Maintain good posture: Sit and stand tall, keep your stomach pulled in and your shoulders back. Poor posture can cause upper back pain.