Osteoporotic Fracture
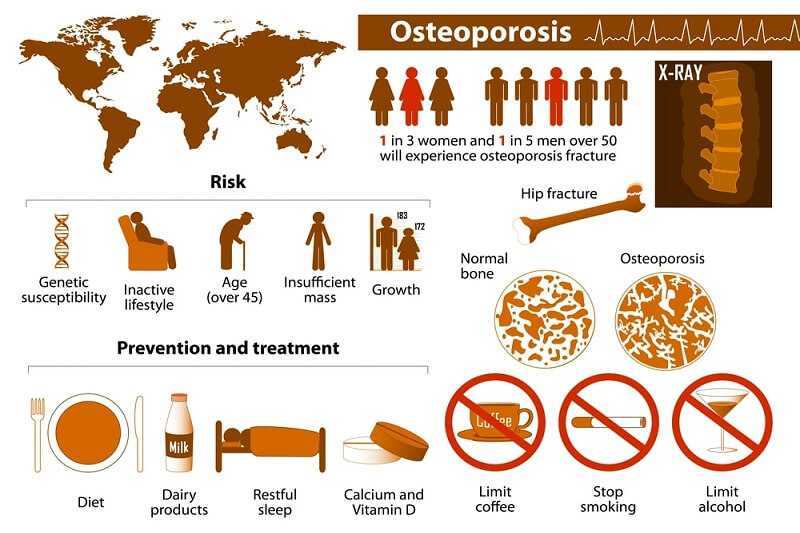
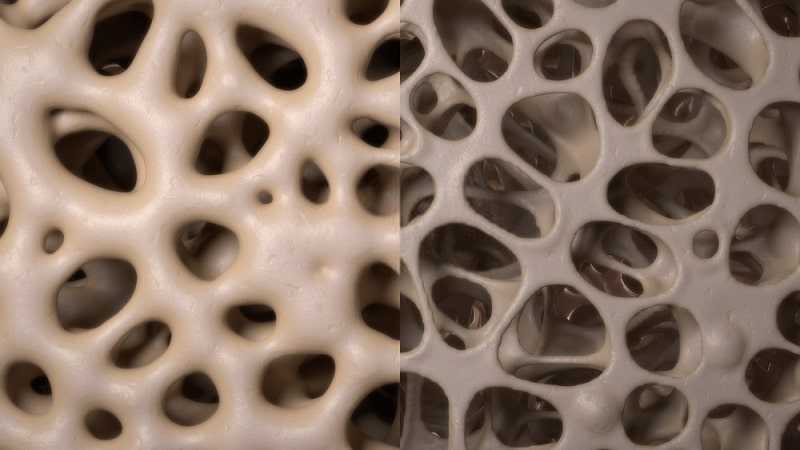
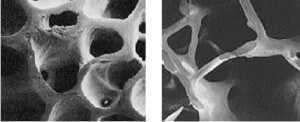
Osteoporosis is a disease that leads to a thinning of the bone, and as such, its main consequence is the increased risk of bone fractures.
Osteoporotic fractures are those that occur in situations where healthy people would not normally break a bone; they are therefore regarded as ‘fragility fractures’. Typical fragility fractures occur in the vertebral column, rib, hip and wrist.
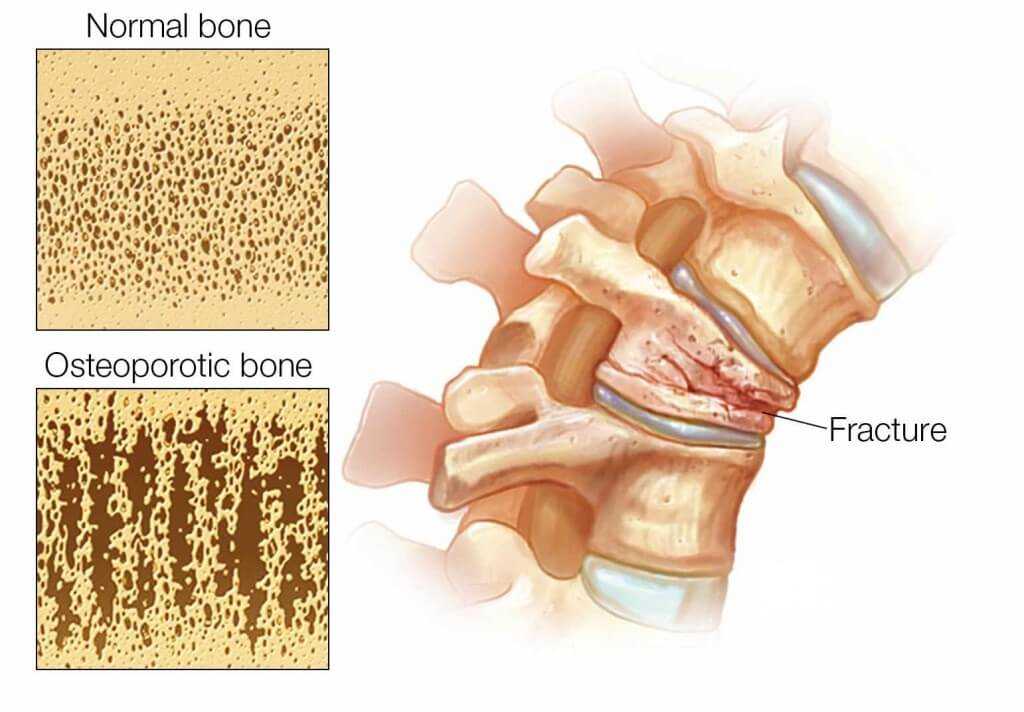
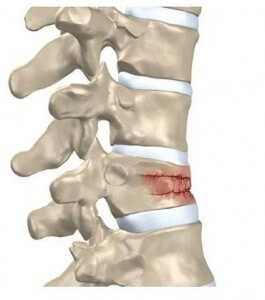
Fractures of the spine are the most dangerous aspect of osteoporosis. Debilitating acute and chronic pain in the elderly is often attributed to fractures of the spine from osteoporosis and can lead to further disability and early mortality. The fractures from osteoporosis may also be asymptomatic.
The symptoms of a vertebral collapse (compression fracture) are sudden back pain, often with radiculopathic pain (shooting pain due to nerve root compression) and rarely with spinal cord compression or cauda equina syndrome. Multiple vertebral fractures lead to a stooped posture, loss of height, and chronic pain with resultant reduction in mobility. There may not be a history of injury.
Symptoms
Osteoporosis is not painful by itself and has no specific symptoms.
However, in the spine, the thoracic and lumbar segments are the most commonly affected. Vertebral compression fractures occur when the bone weakens and can no longer support the load imposed on it. Spinal symptoms related to osteoporosis include back pain and deformity that can lead to a hunched back and/or decreased height.
Treatment
There are several quick and easy screening evaluations for osteoporosis that scan the wrist or heel.
You will also have x-rays of the spine to check for fractures. You will also undergo a bone density scan. Generally the lower spine and hip are scanned. Your bone quality is reported by comparing you to others of the same age and gender as well as to a young adult population. The results are usually considered in terms of your bone being of normal density, somewhat reduced density (called osteopenia) or significantly reduced density (osteoporosis).
Treatments for osteoporosis include supplementation with calcium and Vitamin D. Weight bearing exercise, including walking is also extremely important to build strong bones. Certain medications such as bisphosphonates, oestrogen, raloxifene, calcitonis and parathyroid hormone are available to prevent, reduce or treat osteoporosis
Fracture Treatment
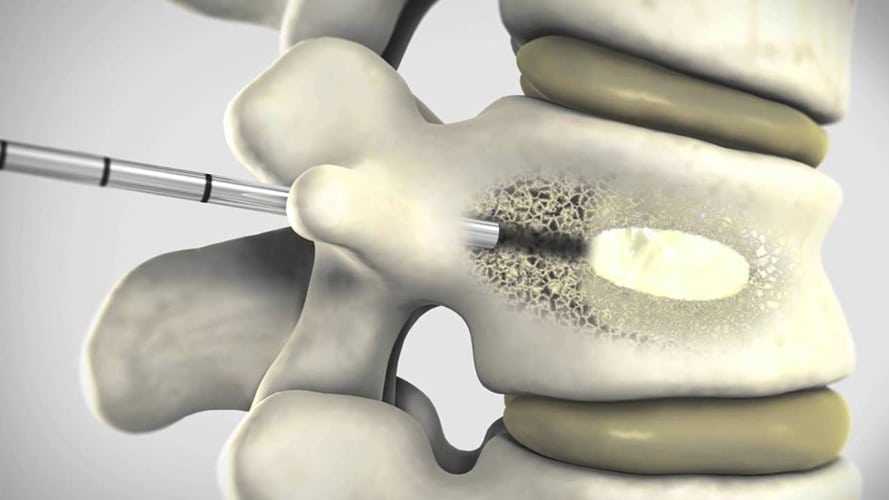
A new treatment called Vertebroplasty has been developed to treat osteoporotic spinal fractures.
A small volume of bone cement is injected into the vertebral body under X-ray control. The treatment is highly effective and safe in experienced hands.