Thoracic Herniated Disc – A More in Depth Look
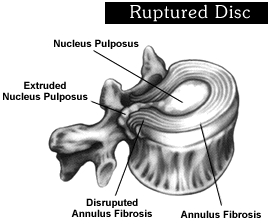
The thoracic herniated disc is located in the upper back. Thoracic herniated discs are not as common as the lumbar or cervical herniated disc. This is because there is generally less pressure and motion in this segment of the spine.
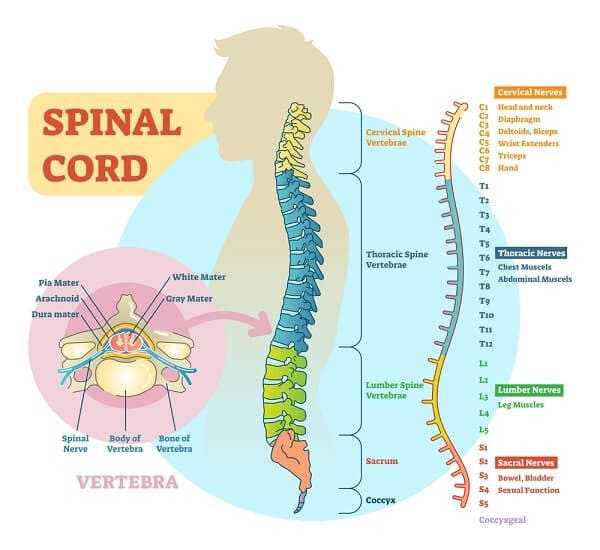
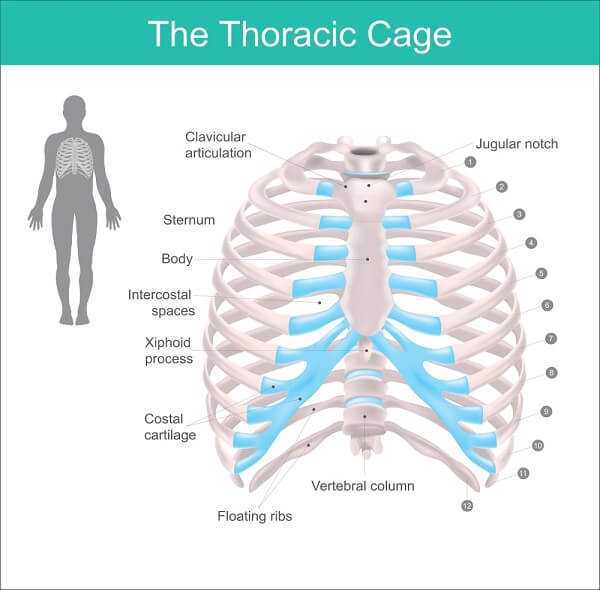
A thoracic herniated disc occurs when the inner gel-like substance of any of the 12 vertebral discs of the thoracic spine leaks out of the inside of the disc. This puts pressure on a nerve root that creates upper back pain along with other symptoms, such as shooting pain or numbness. The type of pain caused will depend on which nerve is receiving this pressure. It will also depend on if the spinal cord itself has pressure being placed on it.
It is important to determine the cause of the thoracic herniated disc before treatment of upper back pain. There are two sources that doctors will look at to determine which course of treatment to take. These causes are classified as:
- Degenerative Disc Disease – Degenerative is associated with a slow and gradual wear and tear of the vertebral discs. This is generally caused with age. It is a very slow process, and patients will usually not feel the effects of the wearing and tearing until long after the onset of the degeneration. Degenerative disc disease will generally be seen in people in their 40’s and 60’s.
Related Article
Degenerative Disc Disease – Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Options
- Thoracic Segment Trauma – When a trauma has occurred to the thoracic region of the back, a herniated disc can develop. Symptoms will develop upon impact. A fall or sports injury causing sudden force to the upper back could be a traumatic event that could lead to a thoracic herniated disc. Younger patients can be exposed to a thoracic segment trauma herniated disc.
Symptoms Associated with the Thoracic Herniated Disc
The symptoms of a thoracic herniated disc will depend on the size and location of the herniated part of the disc. There are general areas that a herniated disc can erupt, which are: central, lateral, or centro-lateral. The symptoms for each are as follows:
- Central Disc Protrusion – There is not much room under the spinal cord in the thoracic spine. Therefore, when there is pressure from the thoracic herniated disc, pressure is put on the spinal cord and can affect this nerve. This type of herniated disc will cause upper back pain. It will depend on the size of the herniated disc and the amount of the pressure on the spinal cord as to the extent of the symptoms. In severe cases, paralysis from the waist down could be a result.
- Herniated Lateral Disc – If a disc protrudes laterally, this is to the side. The gel-like material will put pressure on the nerve that is located at that level of the spine and will likely cause radiation chest wall or abdominal pain.
- Herniated Centro-lateral Disc – A combination of symptoms can occur with this type of thoracic herniated disc. This could be upper back pain, radiating pain, or Myelopathy, which is a functional disturbance or pathological change in the spinal cord.
While the thoracic herniated disc is not as common as the others, it still exists and can be painful. It is important that the type of herniated disc is discovered to ensure proper treatment.