What is a percutaneous discectomy ?
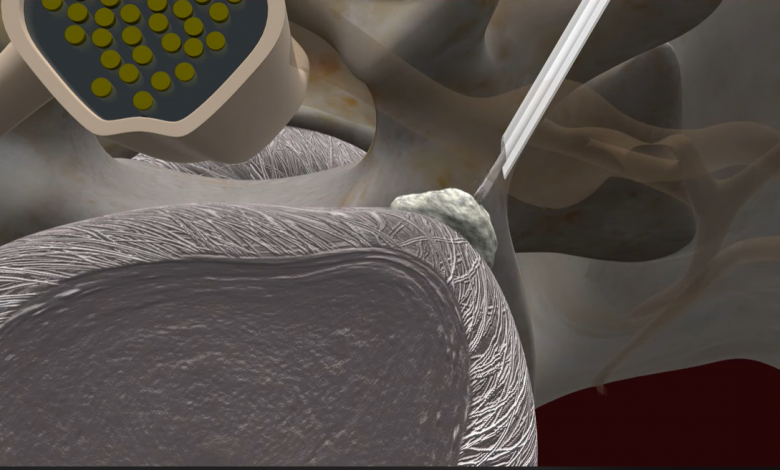
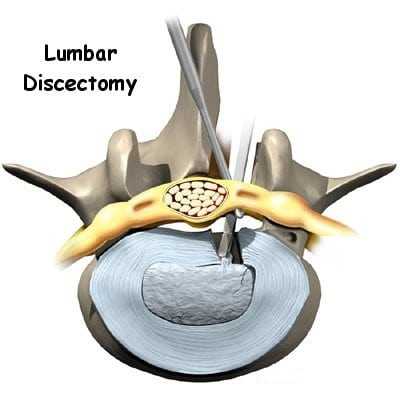
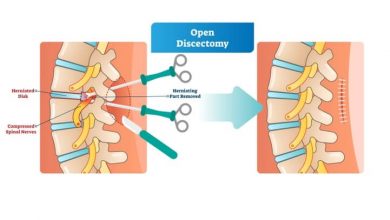
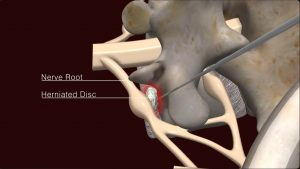
Percutaneous discectomy is a minimally invasive surgical procedure used to treat herniated discs in the spine. This procedure is typically performed under local anesthesia and involves accessing the affected disc through a small incision in the skin.
During the procedure, a surgeon uses fluoroscopy or other imaging techniques to guide specialized instruments, such as a cannula or needle, to the location of the herniated disc. Once the instruments are in place, the surgeon removes or reduces the herniated disc material, relieving pressure on the nearby nerves and reducing symptoms such as pain, numbness, or weakness.
Percutaneous discectomy is often performed on an outpatient basis, meaning the patient can typically go home the same day as the procedure. It generally offers a quicker recovery time and less postoperative pain compared to traditional open surgery for disc herniation. However, not all patients or types of disc herniation are suitable for percutaneous discectomy, and the procedure may not be appropriate in all cases. It’s essential for individuals considering this procedure to discuss their specific condition and treatment options with a qualified healthcare professional.
Percutaneous discectomy offers several advantages over traditional open surgery, including:
a) Minimally invasive
The procedure requires only a small incision, resulting in less trauma to the surrounding tissues and faster recovery times.
- Small Incision: Instead of a large incision as in traditional open surgery, percutaneous discectomy involves making a small incision in the skin, typically less than one inch in length.
- Less Tissue Damage: Because of the smaller incision, there is less disruption to the surrounding muscles, ligaments, and tissues compared to open surgery. This can result in less postoperative pain and faster recovery.
- Reduced Blood Loss: Minimally invasive techniques typically involve less blood loss during the procedure compared to open surgery, leading to a lower risk of requiring blood transfusions.
- Quicker Recovery: Patients who undergo percutaneous discectomy often experience a quicker recovery time compared to traditional open surgery. They may be able to resume normal activities sooner and have a shorter hospital stay, if any.
- Lower Risk of Complications: Minimally invasive procedures generally carry a lower risk of complications such as infection, nerve damage, and blood clots compared to open surgery.
- Outpatient Procedure: Many percutaneous discectomy procedures can be performed on an outpatient basis, meaning patients can go home the same day as the surgery.
Overall, the minimally invasive nature of percutaneous discectomy makes it an attractive option for many patients seeking relief from symptoms associated with disc herniation while minimizing the impact on their daily lives. However, it’s important to note that not all patients or types of disc herniation are suitable for this procedure, and the decision should be made in consultation with a qualified spine specialist.
b) Outpatient procedure:
Most percutaneous discectomies can be performed on an outpatient basis, allowing patients to return home the same day.
- Convenience: Patients can undergo the procedure without the need for an overnight hospital stay, allowing them to return home on the same day and recover in the comfort of their own surroundings.
- Cost-effectiveness: Outpatient procedures generally incur lower healthcare costs compared to surgeries that require an overnight hospital stay.
- Reduced risk of hospital-acquired infections: Since patients are discharged home shortly after the procedure, they are less exposed to potential hospital-acquired infections.
- Faster recovery: Being able to recover at home can contribute to a more comfortable and familiar environment, potentially facilitating a quicker recovery process.
- Minimization of disruption to daily life: Patients can resume their normal activities sooner when they undergo an outpatient procedure, as they do not need to spend additional time in the hospital.
It’s important to note that while percutaneous discectomy is often performed on an outpatient basis, the decision to discharge a patient the same day depends on various factors, including the patient’s overall health, the complexity of the procedure, and the presence of any postoperative complications. Additionally, patients will typically need someone to drive them home after the procedure and may require assistance with activities of daily living during the initial stages of recovery.
c) Reduced risk of complications:
Because the procedure is minimally invasive, there is a lower risk of complications such as infection, blood loss, and nerve damage compared to open surgery.
- Smaller Incision: Percutaneous discectomy involves making a small incision in the skin, typically less than one inch in length. This smaller incision results in less trauma to the surrounding tissues, reducing the risk of complications such as excessive bleeding and tissue damage.
- Less Disruption to Surrounding Structures: The minimally invasive approach of percutaneous discectomy involves accessing the herniated disc through muscle-sparing techniques. This results in less disruption to the muscles, ligaments, and other structures surrounding the spine, potentially reducing the risk of complications such as postoperative pain and muscle weakness.
- Reduced Blood Loss: Minimally invasive techniques typically involve less blood loss during the procedure compared to traditional open surgery. This can lower the risk of complications related to blood loss, such as anemia or the need for blood transfusions.
- Lower Risk of Infection: Minimally invasive procedures generally carry a lower risk of surgical site infections compared to open surgery. The smaller incision size and reduced exposure to the external environment may help minimize the risk of infection.
- Faster Recovery: Due to the minimally invasive nature of percutaneous discectomy, patients often experience a quicker recovery time compared to traditional open surgery. A faster recovery can contribute to a lower risk of complications associated with prolonged immobility or hospitalization.
It’s important to note that while percutaneous discectomy may have a reduced risk of certain complications, there are still potential risks associated with the procedure, including nerve injury, spinal fluid leakage, and recurrence of disc herniation. Patients considering percutaneous discectomy should discuss the potential risks and benefits with their healthcare provider to make an informed decision about their treatment options.
However, percutaneous discectomy may not be suitable for all patients or types of disc herniation. It is essential to consult with a spine specialist to determine the most appropriate treatment approach based on individual circumstances and preferences.