Ozone discectomy
Understanding Ozone Discectomy: An Overview
In recent years, ozone discectomy has emerged as a promising alternative treatment for certain spinal conditions, particularly disc herniation. This minimally invasive procedure involves the injection of ozone gas into the intervertebral disc space to alleviate pain and reduce inflammation. While still gaining recognition within the medical community, ozone discectomy offers several potential benefits compared to traditional surgical interventions. In this article, we delve into the fundamentals of ozone discectomy, exploring its mechanism of action, indications, procedure, and outcomes.
The Science Behind Ozone Discectomy
Ozone, a molecule composed of three oxygen atoms (O3), is well-known for its powerful oxidizing properties. In the context of ozone discectomy, medical-grade ozone gas is injected directly into the affected disc under fluoroscopic guidance. Upon contact with the disc tissue, ozone induces a series of biochemical reactions. It promotes the breakdown of proteoglycans, which are responsible for maintaining the hydration and integrity of the disc. Additionally, ozone triggers the release of anti-inflammatory mediators and growth factors, facilitating tissue repair and regeneration. By targeting the underlying pathology of disc herniation, ozone discectomy aims to relieve compression on spinal nerves and alleviate associated symptoms.
Indications and Patient Selection
Ozone discectomy is primarily indicated for patients with symptomatic disc herniation, particularly those experiencing radicular pain (pain radiating along the path of a nerve). Candidates for this procedure typically undergo a comprehensive evaluation, including a thorough medical history, physical examination, and diagnostic imaging (such as MRI or CT scans). Ideal candidates are individuals who have failed to respond to conservative treatments such as medication, physical therapy, and epidural steroid injections. However, not all patients with disc herniation are suitable candidates for ozone discectomy, and careful patient selection is crucial to ensure optimal outcomes.
Procedure and Technique
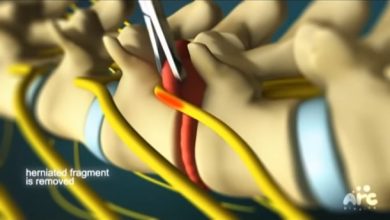
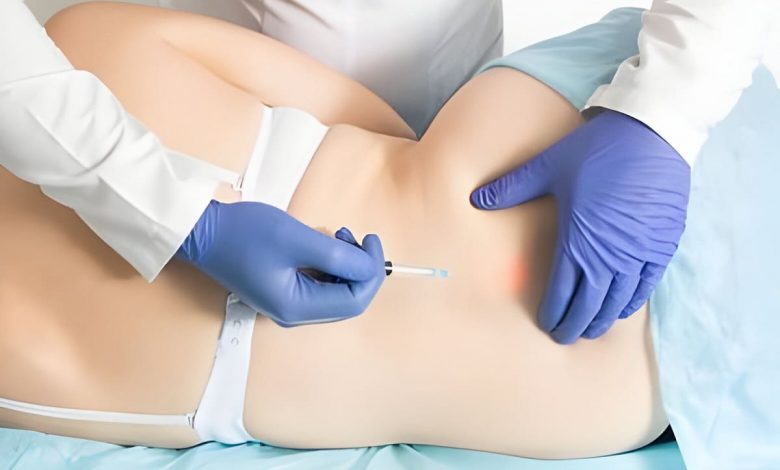
Ozone discectomy is performed on an outpatient basis and usually takes less than an hour to complete. The procedure is carried out under local anesthesia to numb the skin and underlying tissues. Using fluoroscopic guidance, a fine needle is inserted into the target disc space under sterile conditions. Once the needle is accurately positioned, medical-grade ozone gas is slowly injected into the disc. Following the injection, patients are typically monitored for a short period before being discharged home. Most individuals can resume their normal activities shortly after the procedure, although some may experience temporary soreness or stiffness at the injection site.
Comparing Ozone Discectomy to Traditional Treatments
One of the key advantages of ozone discectomy is its minimally invasive nature, which entails smaller incisions, reduced tissue trauma, and shorter recovery times compared to traditional open surgery. Unlike conventional discectomy procedures, ozone discectomy does not involve the removal of disc material or the insertion of implants. As a result, the risk of complications such as infection, bleeding, and spinal instability is significantly lower. Furthermore, ozone discectomy can be performed as a standalone procedure or in conjunction with other minimally invasive techniques, offering a versatile treatment approach for a wide range of patients.
Safety and Efficacy
Numerous clinical studies have demonstrated the safety and efficacy of ozone discectomy in appropriately selected patients. Research suggests that ozone discectomy can lead to significant improvements in pain, function, and quality of life, with minimal risk of adverse effects. However, like any medical procedure, ozone discectomy is not without potential risks and limitations. Common side effects may include transient discomfort at the injection site, mild bruising, or allergic reactions to the anesthesia or ozone gas. In rare cases, complications such as nerve injury or infection may occur, although these are exceedingly rare when the procedure is performed by experienced practitioners using proper techniques.
Conclusion
Ozone discectomy represents a promising advancement in the field of spinal care, offering a safe and effective alternative to traditional surgical interventions for disc herniation. By harnessing the therapeutic properties of ozone gas, this minimally invasive procedure aims to alleviate pain, reduce inflammation, and promote tissue healing without the need for extensive tissue disruption or prolonged recovery periods. While further research is warranted to elucidate its long-term outcomes and refine patient selection criteria, ozone discectomy holds great potential as a valuable addition to the armamentarium of treatments for spinal disorders. As with any medical decision, patients considering ozone discectomy should consult with a qualified healthcare provider to determine the most appropriate course of action based on their individual needs and circumstances.
The Science Behind Ozone Discectomy
Ozone discectomy stands at the forefront of minimally invasive spinal treatments, offering a promising alternative to traditional surgical procedures for disc herniation and related conditions. Central to the success of this innovative approach is the profound biochemical and therapeutic effects of ozone gas on intervertebral disc tissue. In this article, we delve into the intricate science behind ozone discectomy, shedding light on its mechanism of action and the physiological processes that underpin its therapeutic efficacy.
Understanding Ozone: A Powerful Oxidizing Agent
Ozone, a triatomic molecule composed of three oxygen atoms (O3), is well-known for its potent oxidizing properties. In medical applications, ozone gas is produced by passing pure oxygen through a high-voltage electrical discharge. This results in the formation of ozone molecules, which possess remarkable reactivity due to the presence of an unstable oxygen-oxygen bond. Ozone’s ability to readily donate oxygen atoms makes it a powerful oxidizing agent with a wide range of biological effects.
Biochemical Reactions in the Disc
When ozone gas is injected into the intervertebral disc space during a discectomy procedure, it initiates a cascade of biochemical reactions within the disc tissue. One of the primary mechanisms of action involves the breakdown of proteoglycans, which are large molecules responsible for maintaining the hydration and structural integrity of the disc. Ozone’s oxidative properties facilitate the cleavage of glycosaminoglycan chains within proteoglycans, leading to a reduction in disc volume and intradiscal pressure.
Anti-inflammatory and Analgesic Effects
In addition to its effects on disc matrix components, ozone exerts potent anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects within the disc microenvironment. Studies have shown that ozone stimulates the release of anti-inflammatory cytokines such as interleukin-10 (IL-10) and tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α), while inhibiting the production of pro-inflammatory mediators like interleukin-1 beta (IL-1β) and prostaglandins. This anti-inflammatory action helps to mitigate the inflammatory response associated with disc herniation, thereby reducing pain and swelling.
Promotion of Tissue Repair and Regeneration
Beyond its role in reducing inflammation and decompressing neural structures, ozone has been shown to promote tissue repair and regeneration within the intervertebral disc. Ozone therapy stimulates the expression of growth factors such as transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-β) and insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1), which play key roles in cell proliferation, extracellular matrix synthesis, and tissue remodeling. By enhancing the regenerative capacity of disc cells, ozone therapy supports the repair of damaged disc tissue and facilitates the restoration of disc function.
Targeted Delivery and Controlled Dosimetry
One of the advantages of ozone discectomy is its ability to deliver therapeutic agents directly to the site of pathology with precision and control. By utilizing fluoroscopic guidance, healthcare providers can accurately target the affected disc and monitor the distribution of ozone gas in real-time. This targeted approach minimizes off-target effects and allows for the precise modulation of dosage parameters, optimizing therapeutic outcomes while minimizing the risk of adverse effects.
Conclusion: Harnessing the Power of Ozone for Spinal Health
In conclusion, ozone discectomy represents a cutting-edge approach to the management of disc herniation and related spinal disorders. By harnessing the biochemical and therapeutic properties of ozone gas, this minimally invasive procedure offers a multifaceted mechanism of action that targets the underlying pathophysiology of disc herniation. From its ability to reduce disc volume and intradiscal pressure to its anti-inflammatory and regenerative effects, ozone therapy holds great promise as a safe, effective, and scientifically grounded treatment modality for patients suffering from debilitating spinal conditions. As research in this field continues to evolve, the elucidation of ozone’s mechanisms of action will undoubtedly pave the way for further advancements in spinal care and enhance our understanding of its therapeutic potential.
Indications and Patient Selection for Ozone Discectomy
Ozone discectomy has emerged as a minimally invasive and promising treatment option for individuals suffering from certain spinal conditions, particularly disc herniation. However, not all patients with back or neck pain are suitable candidates for this procedure. Understanding the indications and appropriate patient selection criteria for ozone discectomy is essential for optimizing treatment outcomes and patient satisfaction. In this article, we explore the key factors guiding the selection of patients for ozone discectomy and the conditions in which this procedure is most beneficial.
Understanding Disc Herniation and its Symptoms
Disc herniation occurs when the soft, gel-like center of an intervertebral disc protrudes through the tough outer layer, often compressing nearby spinal nerves and causing symptoms such as pain, numbness, tingling, and weakness. These symptoms may radiate along the path of the affected nerve, leading to conditions such as sciatica (pain radiating down the leg) or cervical radiculopathy (pain radiating down the arm). While many cases of disc herniation resolve with conservative treatments such as rest, medication, physical therapy, and epidural steroid injections, some individuals may continue to experience persistent or debilitating symptoms despite these interventions.
Indications for Ozone Discectomy
Ozone discectomy is typically considered for patients with symptomatic disc herniation who have not responded adequately to conservative treatments and continue to experience significant pain and functional impairment. The following are common indications for considering ozone discectomy:
-
Persistent or Severe Pain:
Patients experiencing persistent or severe pain due to disc herniation that significantly impacts their quality of life and daily functioning may be candidates for ozone discectomy.
-
Failed Conservative Treatments:
Individuals who have failed to achieve satisfactory relief from conservative treatments such as medication, physical therapy, or epidural steroid injections may benefit from ozone discectomy as an alternative intervention.
-
Radicular Symptoms:
Patients with radicular symptoms, such as sciatica or cervical radiculopathy, resulting from nerve compression by a herniated disc, may find relief through ozone discectomy, particularly if the symptoms are refractory to other treatments.
-
Disc Herniation with MRI Confirmation:
Confirmation of disc herniation through diagnostic imaging, such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), is typically required to establish the anatomical basis for symptoms and guide treatment decisions.
Patient Selection Criteria
Successful outcomes with ozone discectomy hinge upon appropriate patient selection. Healthcare providers carefully assess patients to determine their suitability for the procedure based on various factors, including:
-
Diagnostic Imaging:
Diagnostic imaging studies, such as MRI or computed tomography (CT) scans, are essential for confirming the presence of disc herniation, assessing its severity, and identifying any associated spinal pathology.
-
Medical History and Physical Examination:
A comprehensive medical history and physical examination help identify underlying medical conditions, assess neurological function, and evaluate the overall health status of the patient.
-
Symptom Duration and Severity:
The duration and severity of symptoms, as well as their impact on the patient’s quality of life and functional status, are important considerations in determining the appropriateness of ozone discectomy.
-
Response to Conservative Treatments:
Patients who have undergone conservative treatments without significant improvement in symptoms may be considered for ozone discectomy, particularly if they meet other selection criteria.
-
Patient Preferences and Expectations:
Patient preferences, expectations, and goals of treatment play a crucial role in decision-making. Open and honest communication between the patient and healthcare provider is essential for aligning expectations and ensuring informed decision-making.
Conclusion
Ozone discectomy offers a minimally invasive and potentially effective treatment option for select patients with symptomatic disc herniation who have not responded to conservative therapies. However, appropriate patient selection is paramount to achieving favorable outcomes and minimizing the risk of complications. By carefully evaluating patient characteristics, symptomatology, diagnostic findings, and treatment goals, healthcare providers can identify suitable candidates for ozone discectomy and tailor treatment plans to meet individual needs. As with any medical intervention, patients considering ozone discectomy should undergo thorough evaluation and consultation with a qualified healthcare provider to determine the most appropriate course of action based on their unique circumstances and preferences.
Procedure and Technique: How Ozone Discectomy Works
Ozone discectomy stands at the forefront of minimally invasive spinal procedures, offering relief to patients suffering from disc herniation and associated symptoms. This innovative technique has garnered attention for its effectiveness and efficiency in addressing spinal conditions while minimizing surgical invasiveness. In this article, we delve into the intricacies of the ozone discectomy procedure, shedding light on its techniques and mechanisms of action.
Understanding the Procedure
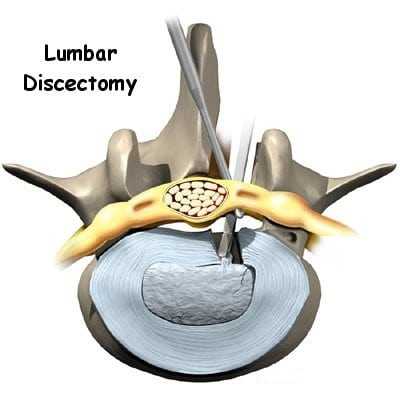
Ozone discectomy involves the precise injection of ozone gas into the affected intervertebral disc. Unlike traditional open surgery, which entails extensive tissue dissection and removal of disc material, ozone discectomy is performed through a small needle under fluoroscopic guidance. This minimally invasive approach minimizes trauma to surrounding tissues and reduces the risk of complications, allowing for quicker recovery and improved patient outcomes.
Preparation and Anesthesia
Before undergoing ozone discectomy, patients typically undergo a thorough evaluation to assess their suitability for the procedure. This evaluation may include a review of medical history, physical examination, and diagnostic imaging studies such as MRI or CT scans to confirm the diagnosis of disc herniation and identify the target disc(s) for treatment.
On the day of the procedure, patients are usually instructed to refrain from eating or drinking for a specified period before the scheduled appointment. Upon arrival at the medical facility, patients are prepped for the procedure and positioned comfortably on the procedure table. Local anesthesia is administered to numb the skin and underlying tissues at the site of needle insertion, ensuring patient comfort throughout the procedure.
Guided Injection Technique
Under fluoroscopic guidance, a thin needle is carefully inserted into the targeted intervertebral disc space. Fluoroscopy provides real-time imaging of the spinal structures, allowing the physician to precisely position the needle and confirm its placement within the disc. Once the needle is properly positioned, medical-grade ozone gas is slowly injected into the disc space.
Mechanism of Action
The therapeutic effects of ozone discectomy are multifaceted and arise from the interaction between ozone gas and the disc tissue. Ozone acts as a potent oxidizing agent, initiating a series of biochemical reactions within the disc. It promotes the breakdown of proteoglycans, which are key components of the disc matrix responsible for maintaining hydration and structural integrity. By reducing the volume of herniated disc material and relieving pressure on spinal nerves, ozone discectomy helps alleviate pain and improve functional outcomes.
Post-Procedure Care
Following the ozone discectomy procedure, patients are typically monitored for a brief period before being discharged home on the same day. Most individuals can resume their normal activities shortly after the procedure, although some may experience mild soreness or stiffness at the injection site. Patients are advised to avoid strenuous activities and heavy lifting for a specified period following the procedure to allow for optimal healing.
Conclusion
Ozone discectomy represents a significant advancement in the treatment of disc herniation, offering a minimally invasive alternative to traditional open surgery. By harnessing the therapeutic properties of ozone gas, this procedure provides effective relief from pain and disability while minimizing surgical invasiveness and reducing the risk of complications. With its proven efficacy and favorable safety profile, ozone discectomy has emerged as a valuable option for patients seeking relief from symptomatic disc herniation. As with any medical procedure, patients considering ozone discectomy should consult with a qualified healthcare provider to determine the most appropriate treatment approach based on their individual needs and circumstances.
Comparing Ozone Discectomy to Traditional Treatments
In the realm of spinal care, the treatment landscape for conditions such as disc herniation has evolved significantly over the years. Traditional surgical interventions, once considered the standard of care, have been supplemented by minimally invasive alternatives like ozone discectomy. This article aims to explore the key differences between ozone discectomy and traditional treatments for disc herniation, shedding light on their respective benefits, drawbacks, and clinical outcomes.
Traditional Treatments for Disc Herniation
Historically, the primary surgical approach for disc herniation has been open discectomy, a procedure involving the removal of herniated disc material through a large incision in the back. While effective in alleviating symptoms and decompressing spinal nerves, open discectomy is associated with certain drawbacks. It typically requires general anesthesia, prolonged hospital stays, and extensive tissue disruption, leading to longer recovery times and increased risk of complications such as infection, bleeding, and spinal instability. Additionally, some patients may experience residual back pain or limited mobility following traditional surgery.
Minimally Invasive Alternatives
In recent years, minimally invasive techniques have gained traction as alternatives to traditional open surgery for disc herniation. These approaches aim to achieve the same therapeutic goals while minimizing tissue trauma, reducing recovery times, and lowering the risk of complications. Among these minimally invasive options, ozone discectomy has emerged as a promising alternative, offering several distinct advantages over traditional treatments.
Key Differences and Advantages of Ozone Discectomy
One of the primary differences between ozone discectomy and traditional treatments lies in their approach to addressing disc pathology. While traditional surgery involves the removal of herniated disc material through a surgical incision, ozone discectomy relies on the injection of medical-grade ozone gas directly into the affected disc space. This minimally invasive technique allows for targeted delivery of therapy without the need for extensive tissue disruption or removal of disc material.
Compared to traditional surgery, ozone discectomy offers several notable advantages:
-
Minimally Invasive Nature
: Ozone discectomy is performed through a small needle insertion, resulting in minimal tissue trauma and reduced risk of complications such as infection and bleeding.
-
Shorter Recovery Times
: Due to its minimally invasive approach, ozone discectomy typically entails shorter recovery times compared to traditional surgery, allowing patients to resume their normal activities sooner.
-
Preservation of Disc Integrity
: Unlike traditional surgery, which involves the removal of disc material, ozone discectomy aims to preserve the structural integrity of the disc while promoting tissue healing and regeneration.
-
Lower Risk of Complications
: Ozone discectomy carries a lower risk of complications such as nerve injury, infection, and spinal instability compared to traditional surgical interventions.
-
Versatility and Adaptability
: Ozone discectomy can be performed as a standalone procedure or in conjunction with other minimally invasive techniques, offering a versatile treatment approach for a wide range of patients.
Clinical Outcomes and Considerations
Numerous clinical studies have evaluated the safety and efficacy of ozone discectomy compared to traditional treatments for disc herniation. While results may vary depending on patient characteristics and study design, research suggests that ozone discectomy can lead to significant improvements in pain, function, and quality of life, with comparable or even superior outcomes to traditional surgery in certain cases. However, further research is needed to elucidate the long-term efficacy and durability of ozone discectomy compared to traditional treatments.
Conclusion
In conclusion, ozone discectomy represents a valuable addition to the armamentarium of treatments for disc herniation, offering a safe, effective, and minimally invasive alternative to traditional surgical interventions. By harnessing the therapeutic properties of ozone gas, this innovative technique aims to alleviate pain, reduce inflammation, and promote tissue healing while minimizing the risks and drawbacks associated with traditional surgery. While both approaches have their merits, ozone discectomy stands out for its potential to deliver comparable or superior clinical outcomes with fewer complications and shorter recovery times. As with any medical decision, patients considering treatment for disc herniation should consult with a qualified healthcare provider to determine the most appropriate course of action based on their individual needs and circumstances.
Safety and Efficacy of Ozone Discectomy: What Research Says
Ozone discectomy, a minimally invasive procedure for treating certain spinal conditions, has garnered increasing attention in recent years. As with any medical intervention, understanding its safety and effectiveness is paramount. In this article, we delve into the current body of research surrounding ozone discectomy, exploring its safety profile, efficacy, and potential advantages compared to traditional treatments.
Safety Considerations
Ensuring patient safety is a fundamental aspect of any medical procedure, and ozone discectomy is no exception. Numerous clinical studies have investigated the safety of ozone discectomy, with findings consistently indicating a low risk of adverse events when performed by experienced practitioners using proper techniques.
One of the primary safety concerns associated with ozone discectomy is the risk of infection. However, meticulous sterile technique and adherence to infection control protocols can mitigate this risk. Additionally, the use of medical-grade ozone gas minimizes the likelihood of allergic reactions or systemic toxicity.
Other potential complications of ozone discectomy include transient discomfort at the injection site, mild bruising, or temporary exacerbation of symptoms. Serious complications such as nerve injury or spinal instability are exceedingly rare but can occur, particularly in cases where the procedure is performed by inexperienced practitioners or inappropriately selected patients.
Efficacy and Outcomes
Numerous clinical studies have evaluated the efficacy of ozone discectomy in alleviating symptoms associated with disc herniation, such as back pain, leg pain, and functional impairment. Overall, research findings suggest that ozone discectomy can lead to significant improvements in pain relief, functional outcomes, and quality of life for appropriately selected patients.
A systematic review and meta-analysis published in the journal Pain Physician in 2020 examined the outcomes of ozone discectomy in patients with lumbar disc herniation. The analysis, which included data from multiple randomized controlled trials and observational studies, found that ozone discectomy was associated with superior pain relief and functional outcomes compared to conservative treatments such as medication and physical therapy. Furthermore, the incidence of adverse events was low, supporting the safety and tolerability of the procedure.
Another study published in the European Spine Journal in 2019 compared the long-term outcomes of ozone discectomy versus traditional surgical discectomy for the treatment of lumbar disc herniation. The findings revealed comparable efficacy between the two procedures in terms of pain relief and functional improvement. However, ozone discectomy was associated with shorter hospital stays, quicker recovery times, and lower rates of postoperative complications.
Advantages of Ozone Discectomy
Ozone discectomy offers several potential advantages over traditional surgical interventions for disc herniation. Its minimally invasive nature entails smaller incisions, reduced tissue trauma, and shorter recovery periods, allowing patients to return to their normal activities more quickly. Additionally, ozone discectomy can be performed on an outpatient basis under local anesthesia, eliminating the need for hospitalization and general anesthesia in most cases.
Furthermore, ozone discectomy targets the underlying pathology of disc herniation by promoting tissue repair and regeneration, rather than simply removing herniated disc material. This approach may lead to more durable and sustainable outcomes, with lower rates of recurrent disc herniation.
Conclusion
The available evidence suggests that ozone discectomy is a safe and effective treatment option for select patients with symptomatic disc herniation. While further research is needed to elucidate its long-term outcomes and compare it to alternative treatments, the existing literature supports the use of ozone discectomy as a valuable addition to the armamentarium of interventions for spinal disorders.
As with any medical procedure, patient selection and procedural technique are critical determinants of outcomes. Patients considering ozone discectomy should undergo a comprehensive evaluation by a qualified healthcare provider to determine the most appropriate course of treatment based on their individual needs and circumstances. By weighing the potential benefits and risks in conjunction with the latest scientific evidence, patients and healthcare providers can make informed decisions regarding the use of ozone discectomy in the management of disc herniation and related spinal conditions.
Recovery and Rehabilitation After Ozone Discectomy
Ozone discectomy has emerged as a minimally invasive and promising treatment option for individuals suffering from disc herniation and associated spinal conditions. While the procedure itself is relatively quick and straightforward, proper recovery and rehabilitation play crucial roles in optimizing outcomes and ensuring long-term success. In this article, we delve into the recovery process following ozone discectomy, including post-procedural care, rehabilitation strategies, and expected timelines for returning to normal activities.
Immediate Post-Procedural Care
Following ozone discectomy, patients are typically monitored for a short period in a recovery area before being discharged home on the same day. Although the procedure is minimally invasive, some individuals may experience mild discomfort or soreness at the injection site. This discomfort is usually temporary and can be managed with over-the-counter pain relievers as recommended by the healthcare provider.
It’s essential for patients to follow any specific post-procedural instructions provided by their healthcare team. This may include avoiding strenuous activities, lifting heavy objects, or driving for a designated period following the procedure. Additionally, patients should keep the injection site clean and dry to reduce the risk of infection.
Gradual Return to Normal Activities
While recovery experiences may vary from person to person, most individuals can resume light activities within a few days to a week after ozone discectomy. However, it’s essential to avoid activities that could strain the back or exacerbate symptoms during the initial recovery period. Patients should gradually increase their activity levels as tolerated, listening to their bodies and avoiding pushing themselves too hard too soon.
Physical therapy or rehabilitation exercises may be recommended to help improve strength, flexibility, and posture. These exercises are typically tailored to the individual’s specific needs and may include gentle stretching, core stabilization exercises, and low-impact aerobic activities. Engaging in regular exercise can promote healing, prevent muscle deconditioning, and reduce the risk of recurrent disc herniation.
Long-Term Recovery and Follow-Up
While many patients experience significant relief from symptoms shortly after ozone discectomy, it’s essential to recognize that full recovery may take time. Some individuals may continue to experience improvements in pain and function over the weeks and months following the procedure.
Regular follow-up appointments with the healthcare provider are essential to monitor progress, address any concerns or complications, and adjust the treatment plan as needed. During these follow-up visits, imaging studies such as MRI or CT scans may be performed to evaluate the success of the procedure and track changes in the spine over time.
Precautions and Lifestyle Modifications
To optimize long-term outcomes and reduce the risk of recurrent disc herniation, patients are often advised to adopt certain lifestyle modifications and precautions. This may include maintaining a healthy weight, practicing good posture, using proper body mechanics when lifting or bending, and avoiding activities that place excessive strain on the spine.
Additionally, patients should be mindful of their overall spine health and take steps to prevent future injury or degeneration. This may involve incorporating regular exercise, eating a balanced diet rich in nutrients that support bone and tissue health, and avoiding smoking, which can impair circulation and hinder healing.
Conclusion
Recovery and rehabilitation following ozone discectomy are integral components of the treatment process. By following post-procedural instructions, gradually returning to normal activities, and engaging in appropriate rehabilitation exercises, patients can optimize their outcomes and regain function and quality of life. With proper care and adherence to lifestyle modifications, many individuals can experience long-lasting relief from symptoms and enjoy improved spinal health after ozone discectomy. As always, it’s essential for patients to maintain open communication with their healthcare providers and seek guidance if they have any questions or concerns during the recovery process.
Potential Risks and Complications of Ozone Discectomy
Ozone discectomy has gained recognition as a minimally invasive treatment option for certain spinal conditions, offering promising results with fewer risks compared to traditional surgical interventions. However, like any medical procedure, ozone discectomy carries potential risks and complications that patients should be aware of before undergoing treatment. In this article, we explore the possible adverse outcomes associated with ozone discectomy and the measures taken to mitigate these risks.
Infection
Infection is a potential risk following any invasive procedure, including ozone discectomy. While the risk of infection is relatively low, proper sterile technique and adherence to infection control protocols are essential to minimize this risk. Healthcare providers take precautions to maintain a sterile environment during the procedure and ensure that the injection site is properly cleaned and disinfected. Patients are also instructed to monitor the injection site for signs of infection, such as redness, swelling, or increased pain, and to seek prompt medical attention if any concerns arise.
Nerve Injury
Although rare, nerve injury is a potential complication of ozone discectomy. The procedure involves the insertion of a needle into the affected disc space, which carries a small risk of inadvertently damaging nearby nerves or spinal structures. To mitigate this risk, healthcare providers use fluoroscopic guidance to accurately position the needle and monitor its placement throughout the procedure. Additionally, patients may experience temporary numbness, tingling, or weakness in the legs following ozone discectomy, which typically resolves spontaneously within a few days to weeks.
Allergic Reactions
Some patients may experience allergic reactions to the anesthesia or ozone gas used during the procedure. While allergic reactions are rare, healthcare providers take precautions to minimize this risk by conducting thorough medical screenings and assessing patients for any known allergies or sensitivities. Patients are advised to inform their healthcare provider of any allergies or adverse reactions to medications or medical substances beforehand to ensure appropriate precautions are taken.
Exacerbation of Symptoms
In some cases, patients may experience a temporary exacerbation of symptoms following ozone discectomy. This may include increased pain, swelling, or discomfort at the injection site or in the surrounding area. While these symptoms are typically mild and transient, patients are encouraged to report any concerns to their healthcare provider for further evaluation and management. In most cases, symptomatic relief is achieved within a few days as the body heals and inflammation subsides.
Recurrence of Symptoms
While ozone discectomy can provide significant relief from symptoms associated with disc herniation, there is a possibility of symptom recurrence over time. Factors such as underlying degenerative changes in the spine, lifestyle factors, and individual anatomy may contribute to recurrent disc herniation or the development of new spinal issues. Patients are encouraged to maintain a healthy lifestyle, including regular exercise, proper body mechanics, and weight management, to reduce the risk of recurrence and promote spinal health.
Conclusion
While ozone discectomy offers several advantages over traditional surgical interventions, it is essential for patients to understand the potential risks and complications associated with the procedure. By working closely with their healthcare providers and following post-procedural instructions, patients can minimize their risk of adverse outcomes and optimize their recovery experience. As with any medical procedure, open communication between patients and healthcare providers is crucial for addressing concerns, managing expectations, and ensuring the best possible outcomes.
Future Directions and Innovations in Ozone Discectomy
Ozone discectomy has rapidly emerged as a minimally invasive and effective treatment option for individuals suffering from disc herniation and related spinal conditions. While the procedure has already revolutionized the field of spinal care, ongoing research and technological advancements continue to shape its future direction. In this article, we explore the latest innovations and potential developments in ozone discectomy that hold promise for improving outcomes and expanding its applications.
1. Advanced Imaging Techniques
One of the key areas of innovation in ozone discectomy lies in the advancement of imaging technologies. High-resolution imaging modalities such as MRI and CT scans provide detailed anatomical information, allowing healthcare providers to precisely identify and target the source of disc pathology. Additionally, real-time imaging techniques, such as fluoroscopy and ultrasound, enable healthcare providers to visualize the procedure as it unfolds, ensuring accurate needle placement and optimal delivery of ozone gas.
2. Targeted Drug Delivery Systems
Recent advancements in targeted drug delivery systems hold promise for enhancing the therapeutic effects of ozone discectomy. By encapsulating ozone-releasing agents within biocompatible carriers, researchers aim to prolong the release of ozone gas within the disc space, maximizing its anti-inflammatory and analgesic properties. These novel drug delivery systems have the potential to improve treatment outcomes, reduce the frequency of repeat procedures, and minimize the risk of systemic side effects.
3. Biomaterials and Tissue Engineering
The integration of biomaterials and tissue engineering approaches represents another exciting frontier in ozone discectomy. Researchers are exploring the use of biocompatible scaffolds and injectable hydrogels to support disc regeneration and repair following ozone treatment. These biomaterials provide a scaffold for cell growth and tissue formation, promoting the restoration of disc height and biomechanical function. Additionally, the incorporation of growth factors and bioactive molecules into these scaffolds may further enhance tissue healing and regeneration.
4. Personalized Medicine and Patient-Specific Treatment Protocols
Advances in personalized medicine and predictive analytics offer the potential to tailor ozone discectomy treatment protocols to the individual characteristics and needs of each patient. By integrating clinical data, imaging findings, and genetic information, healthcare providers can develop personalized treatment plans that optimize outcomes and minimize the risk of adverse events. Predictive modeling techniques may also help identify patients who are most likely to benefit from ozone discectomy, enabling more precise patient selection and improved treatment efficacy.
5. Minimally Invasive Techniques and Robotics
Continued refinement of minimally invasive techniques and the integration of robotic-assisted technologies are poised to further enhance the safety and precision of ozone discectomy procedures. Robotic systems offer unparalleled accuracy in needle placement and controlled delivery of ozone gas, reducing the risk of procedural complications and optimizing treatment outcomes. Additionally, minimally invasive approaches minimize tissue trauma, shorten recovery times, and improve patient satisfaction compared to traditional open surgery.
Conclusion
The future of ozone discectomy is brimming with promise, driven by ongoing research, technological innovations, and a growing understanding of spinal pathophysiology. By leveraging advanced imaging techniques, targeted drug delivery systems, biomaterials, personalized medicine, and robotic-assisted technologies, healthcare providers are poised to revolutionize the treatment of disc herniation and related spinal conditions.
As these innovations continue to evolve, the landscape of spinal care will undoubtedly be transformed, offering new avenues for improving patient outcomes, reducing healthcare costs, and enhancing quality of life. While challenges and hurdles may arise along the way, the collective efforts of researchers, clinicians, and industry partners will undoubtedly propel ozone discectomy forward as a cornerstone of modern spinal therapy.
Conclusion: The Role of Ozone Discectomy in Spinal Care
Ozone discectomy has emerged as a revolutionary approach in the realm of spinal care, offering a minimally invasive and effective treatment option for individuals grappling with disc herniation and associated spinal conditions. As we conclude our exploration into this innovative procedure, it becomes evident that ozone discectomy holds a significant and evolving role in the landscape of spinal therapy. In this final segment, we reflect on the key insights gleaned and the future prospects of ozone discectomy in enhancing patient outcomes and shaping the future of spinal care.
A Paradigm Shift in Treatment Approach
Traditionally, the management of disc herniation and spinal disorders often involved invasive surgical interventions with prolonged recovery times and potential risks of complications. Ozone discectomy represents a paradigm shift in this approach, offering a minimally invasive alternative that prioritizes patient safety, comfort, and rapid recovery. By harnessing the therapeutic properties of ozone gas, this procedure aims to alleviate pain, reduce inflammation, and promote tissue healing without the need for extensive tissue disruption or prolonged hospitalization.
Efficacy and Safety
Numerous clinical studies and real-world experiences attest to the efficacy and safety of ozone discectomy in appropriately selected patients. Research findings consistently demonstrate significant improvements in pain relief, functional outcomes, and quality of life following ozone discectomy, with low rates of procedural complications. Moreover, advancements in imaging technologies, targeted drug delivery systems, and minimally invasive techniques continue to enhance the precision and effectiveness of ozone discectomy, further solidifying its role as a cornerstone of modern spinal therapy.
Expanding Applications and Innovations
The applications of ozone discectomy extend beyond the treatment of disc herniation to encompass a broad spectrum of spinal conditions, including degenerative disc disease, spinal stenosis, and facet joint syndrome. Ongoing research and technological innovations promise to further expand the utility and efficacy of ozone discectomy in addressing these diverse pathologies. From personalized treatment protocols to biomaterials and robotics, the future holds immense potential for refining and optimizing the delivery of ozone therapy in spinal care.
Patient-Centered Care
At the heart of ozone discectomy lies a commitment to patient-centered care, where individual needs, preferences, and outcomes take precedence. By tailoring treatment plans to the unique characteristics and circumstances of each patient, healthcare providers can optimize outcomes, minimize risks, and improve overall patient satisfaction. Moreover, patient education and empowerment play a crucial role in fostering collaboration, shared decision-making, and long-term success in managing spinal conditions with ozone discectomy.
Looking Ahead
As we look ahead, the role of ozone discectomy in spinal care is poised to continue evolving, driven by ongoing research, technological advancements, and a deepening understanding of spinal pathophysiology. While challenges and obstacles may arise, the collective efforts of researchers, clinicians, and industry partners will undoubtedly propel ozone discectomy forward as a cornerstone of modern spinal therapy. By embracing innovation, collaboration, and patient-centered care, we can unlock the full potential of ozone discectomy in improving the lives of individuals grappling with spinal disorders worldwide.
In conclusion, ozone discectomy stands as a beacon of hope and innovation in the field of spinal care, offering a safe, effective, and minimally invasive treatment option for individuals seeking relief from disc herniation and related spinal conditions. As we embark on this transformative journey, let us remain steadfast in our commitment to advancing spinal therapy and improving the quality of life for patients around the globe.