Anterior Cervical Discectomy with Fusion
Anterior Cervical Discectomy with Fusion is a type of surgery that may remove a herniated spinal disc in the neck area. Anterior Cervical Discectomy with Fusion is a type of surgery that relieves the pains that could be associated with the neck and arms. Anterior Cervical Discectomy with Fusion is good for patients who may be experiencing pain traveling within the arms or who encounter a partial paralysis in the arms and legs which could occur below a spinal cord compression. Anterior Cervical Discectomy with Fusion is performed within the neck area, preferable the front of the neck, where a disc will be removed and replaced with a graft that fuses the vertebral bodies with a metal plate to help secure the discs in its proper place.
Anterior cervical discectomy with fusion will usually be performed to help with any pain that is associated within the arms and neck. Anterior cervical discectomy with fusion could also be performed to prevent the worsening of paralysis that a patient may be experiencing with cases of spinal cord compression. Anterior cervical discectomy with fusion surgery is performed by a neurosurgeon who will make the incision within the front of the spine. The neurosurgeon will then remove the disc and prepare the plates of the vertebral body which will accept a graft and a type of fusion from one vertebrate to another. The neurosurgeon will place a metal plate over the interspace to make sure their is enough stability so that the bone has a chance to fuse together. The neurosurgeon will finally close the incision with sutures and glue, once it has been determined with an intraoperative x-ray, that the positioning of the instrumentation is in its proper place.
Patients are usually sent home the day after their anterior cervical discectomy with fusion surgery and should keep their wound clean until the neurosurgeon has given them the ok to get it wet. The risks of an anterior cervical discectomy with fusion surgery are fairly low, but their are some potential risk that patients should be aware of and those are bleeding, infection, injury to nerves within the neck, trouble with speech and swallowing, spinal cord injury, paralysis and death.
Artificial Cervical Disc Replacement
Artificial cervical disc replacement is a type of surgery that replaces the spinal discs in your neck. Artificial cervical disc replacement may be needed when a patient is experiencing pain in the neck or arms because of a herniated disc that is pressing on the spinal cord or on the nerves that travel throughout the arms. Artificial cervical disc replacement may also be necessary if a patient is experiencing a pain that is traveling down the arms because of a compressed nerve or when the patient is encountering a partial paralysis below the spinal cord compression from the spinal disc.
An artificial cervical disc replacement surgery will need to be performed through the front of the neck, which is where the disc will be removed and replaced with an artificial disc. Artificial cervical disc replacement surgery will allow the patient to have some type of motion preservation throughout the adjacent vertebral bodies.
An artificial cervical disc replacement surgery can be performed to help patients with neck and arm pain. An artificial cervical disc replacement surgery will help to preserve the motion of the patients neck or arms. artificial cervical disc replacement surgery will be performed by a neurosurgeon, where the neurosurgeon will prepare the front of the neck for surgery. The neurosurgeon will then make an incision in the neck, where they can reach the front of the spine. The neurosurgeon will remove the spinal disc and then place the artificial disc within the disc space. The incision will be closed with closed with sutures and the skin will then be closed with glue.
Patients who undergo artificial cervical disc replacement surgery will generally be discharged the day after the surgery where the patient will be given instructions on keeping the wound clean and dry until the neurosurgeon says that it is ok to get it wet. An artificial cervical disc replacement surgery has some risk involved and those can include bleeding, infection, trouble swallowing, paralysis and even death.
Balloon Kyphoplasty Procedure
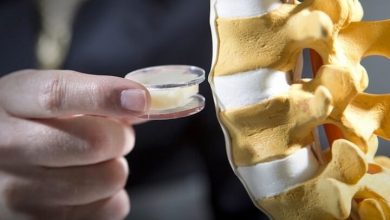
A balloon kyphoplasty procedure is a type of surgery that is usually performed by a neurosurgeon, where osteoporosis is having a dramatic impact on the spine. A balloon kyphoplasty procedure can help patients who are experiencing significant compression fractures, which can occur with osteoporosis, which could help alleviate lower back pain and helps patients avoid having to wear a back brace. A balloon kyphoplasty procedure was developed so that a neurosurgeon can expand some of the compression on the bone of the spine and then the neurosurgeon can fill the cavity with spinal bone cement. A balloon kyphoplasty procedure helps to restore the angulation of the spine to restore height and relieve the back pain that a patient may be experiencing. The success rate of a balloon kyphoplasty procedure is proven to be very good.
A balloon kyphoplasty procedure can be done if a patient is experiencing back pain that could be associated with compression of the spine from the effects of osteoporosis. The procedure of a balloon kyphoplasty first consists of an anesthesiologist putting the patient to sleep. The patient is positioned on their stomach and the back area is prepared in a sterile manner. The neurosurgeon will use a live x-ray during the balloon kyphoplasty procedure with two different machines at the same time so that the neurosurgeon can have a visualization of the procedure.
The neurosurgeon will place a needle and a drill into the vertebra, where the neurosurgeon will pass a balloon into the compressed area to expand the vertebra to fix the angulation and the loss of height of the spine. The neurosurgeon will finally inject some cement in the vertebra, where the cement will harden within a few minutes and the neurosurgeon can release the needles and close the skin with glue.
The postoperative care of a balloon kyphoplasty procedure can consist of the patient usually being discharged between an hour or two after the procedure, but the patient will need to make sure that someone else is there to take them home. The patient will also need to make sure that the sites where the surgery was done is kept clean and dry. The risks of a balloon kyphoplasty procedure are fairly low and some of those risks could consist of bleeding, infection, nerve injury, spinal cord injury, embolization of cement into the veins and lungs and even death.
Invasive Percutaneous Spine Surgery
Invasive percutaneous spine surgery is a type of surgery of the spine that can be performed either through an open surgical approach or an invasive approach. Invasive percutaneous spine surgery can have some advantages to having a lumbar surgery performed through the invasive approach such as a smaller incision during the surgery, less of a stay in the hospital, and less pain medication that will be needed while in the hospital.
Invasive percutaneous spine surgery is different from an open surgical approach because it allows the neurosurgeon to achieve the same type of operative goals but in a less invasive way. The technology for invasive percutaneous spine surgery will continue to improve and this will allow for more neurosurgeon’s to use this technique in certain lumbar procedures. Patients will want to ask their neurosurgeon which option is best for them.
Invasive percutaneous spine surgery has been shown to offer patients some great benefits when it comes to deciding on whether or not this type of surgery is best for them. These benefits include less stress, a shorter hospital stay, a smaller scar, less damage to the skin or muscle, faster rehabilitation, and a quicker return time to any normal activities. The procedure of invasive percutaneous spine surgery is the neurosurgeon will be able to make smaller incisions and the neurosurgeon will also be able to spread the muscle fibers away from the bone instead of stripping it as is the case in an open surgery.
The neurosurgeon will need to have the guidance of an x-ray machine that will be used more intensively during this type of invasive spine surgery, which will allow for the neurosurgeon to guide through certain points with smaller incisions on the skin. Invasive percutaneous spine surgery will further allow the neurosurgeon to decide on which type of situations can be treated through an invasive approach or with a open approach.
The postoperative care for an invasive percutaneous spine surgery is there is usually a shorter hospital stay and the patient will need to keep the incision clean and dry for up to ten to twelve days. Much like open surgery, an invasive surgery will have some risks that could result in possible damage to the nerves in the area of the invasive surgery.
Lumbar Discectomy Surgery
Lumbar discectomy surgery is a type of surgery that helps to remove the pressure on a nerve in the lower back region that could be caused by a herniated disc. Lumbar discectomy surgery allows for a small amount of bone in the lower back region to be removed so that the neurosurgeon can gain access to the affected nerve. Lumbar discectomy surgery allows the neurosurgeon to gently push aside the nerve and then the disc that is pushing into the affected is removed.
Lumbar discectomy surgery is done through a small incision in the lower back region with a microscope to provide the most optimal visualization of the affected nerves. Lumbar discectomy surgery can also be performed with a standard incision in the midline of the back or through a tube that is inserted through the skin.
Lumbar discectomy surgery is usually performed on patients who may need help to relieve their leg pains that could be caused by a herniated disc in the lower back region. The procedure of how lumbar discectomy surgery works is first an anesthesiologist will put the patient to sleep. The patient will be carefully turned onto their stomach to protect all of the necessary pressure points. An x-ray may be used to help guide the placement of the incision, where the incision will be made within or slightly off the mid-line of the back. Once the back of the spine is identified, a portion will be removed and a ligament against the nerve will be partially removed.
Lumbar discectomy surgery will remove the herniated disc and any other disc fragments will also be removed at this time. Once the neurosurgeon assesses the decompression of the nerve roots, it will be irrigated with antibiotics and then the incision will be closed up. The postoperative care of lumbar discectomy surgery is most patients will usually be discharged the same day or the following day after surgery. After lumbar discectomy surgery, a patient may feel some numbness in the leg, twinges in the leg, pain around the incision, and/or some spasms of the back muscles. All of these symptoms should improve within one to two weeks after lumbar discectomy surgery.
Lumbar Endoscopic Discectomy Surgery
Lumbar endoscopic discectomy surgery is a type of invasive surgical procedure that removes a portion of a disc, which will decompress the nerves in the lumber spine. Lumbar endoscopic discectomy surgery can be performed through a tube that is a few millimeters in diameter, when the entry site of the tube is toward the backside. Lumbar endoscopic discectomy surgery can allow a neurosurgeon to gain the needed access to the disc space without having to make a bigger incision to pull back and retract the muscles of the back.
Lumbar endoscopic discectomy surgery can be performed to help reduce the pain in the lower pain or take the pressure off a nerve in the lumbar spine. The procedure of how a lumbar endoscopic discectomy surgery works is first the patient is brought to the operating room and placed on their stomach. The patient will be lightly sedated in order to make the procedure as pleasant as possible. The puncture site is then made on the side of the back in order to pass the scope and any other instruments that are needed in the disc space.
The neurosurgeon will begin to remove some of the disc substance. Once the operation is done, the scope will be removed and the incision is closed. Sometimes, there may be a need to put incisions on both of sides of the back so that the scope can be used on both sides. The postoperative care of lumbar endoscopic discectomy surgery is patients are usually discharged the same day of the surgery. The pain in the low back or legs will improve, but the patient may still experience some numbness or tingling in the legs.
During the healing process, patients are urged not bend, lift, or twist for a few weeks after the lumbar endoscopic discectomy surgery. The risks of lumbar endoscopic discectomy surgery are fairly low, but patients need to keep in mind some of the potential risks such as bleeding, infection, nerve injury, and recurrence of a disc herniated at the same level as before.
Lumbar Facetectomy Surgery
Lumbar facetectomy surgery is considered to be a surgical procedure that helps to decompress the pressure on the nerves of the spine by the facet joints that may be irritating them. Lumbar facetectomy surgery is a minimally invasive procedure that could be combined with a spinal fusion if stability becomes an issue with a facet joint removal. Lumbar facetectomy surgery tries to treat the pain and any other symptoms by removing the affected facet joints.
Lumbar facetectomy surgery is usually performed on patients who need to relieve any leg or arm pain they may be experiencing. The procedure of how lumbar facetectomy surgery works is first the patient is put to sleep by an anesthesiologist. The patient will be carefully turned onto their stomach in order to protect their pressure points. Once antibiotics are given to the patient, an x-ray machine may be used to help the neurosurgeon on where to place the incision, which is usually the midline of the back.
The neurosurgeon will then remove a portion of either a disc, bone spur or ligament to help decompress the nerve of the spine as it leaves the neural foramen. A neurosurgeon will use micro-instruments in order to make sure that the nerves of the spine are free. Finally, the incision is irrigated with antibiotics and closed. The postoperative care of lumbar facetectomy surgery is the patient may have to stay in the hospital for a day or two.
Patients of lumbar facetectomy surgery should keep their incisions dry and clean for at least seven to ten day or until your neurosurgeon gives you the go ahead. After the surgery and during the recovery, patients should avoid any bending, lifting, or twisting for up to four to six weeks. Depending on what kind of work that the patient does, they may usually return to work within two to four weeks.
Lumbar Foraminotomy Surgery
Lumbar foraminotomy surgery is a type of procedure that could be performed on patients who need to have pressure relieved on a nerve that is being compressed when it exits the spinal canal. Sometimes, nerves will leave the canal of the spine through small openings, where the nerves can be compressed, because of a disc protrusion, bone spur, or a thickened ligament. Lumbar foraminotomy surgery can further help patients who are experiencing any type of pain traveling down the arms or legs of a compressed nerve root.
Lumbar foraminotomy surgery is performed on patients who are looking to get some type of relief from arm or leg pain. The procedure of how lumbar foraminotomy surgery works is first the patient will be put to sleep by an anesthesiologist and then the patient is carefully turned onto their abdomen in the operating room to protect all of the pressure points in the back. Antibiotics are given to the patient at this point and an x-ray is used to determine the best place for the incision, which would usually be in the midline of the back. Lumbar foraminotomy surgery exposes the roof of the spinal canal, where the neurosurgeon will remove a portion of a disc or bone spur to help decompress the nerve as it leaves the foramen.
Once the surgery is done, the incision is soaked with antibiotics and closed. The postoperative care of lumbar facetectomy surgery is the patient may be released the same day or the next day following surgery. Patients of lumbar foraminotomy surgery should keep their incisions dry and clean for at least seven to ten day or until your neurosurgeon gives you the go ahead. After the surgery and during the recovery, patients should avoid any bending, lifting, or twisting for up to four to six weeks. Depending on what kind of work that the patient does, they may usually return to work within two to four weeks. The risks of lumbar foraminotomy surgery are usually pretty low, but there are some risks that a patient should be aware of such as bleeding, infection, nerve injury, and spinal fluid leaks.
Lumbar Spinal Fusion Surgery
Lumbar spinal fusion surgery is a type of procedure that is performed for patients who are experiencing some sort of back pain to help immobilize the adjacent vertebrae or a number of vertebrae in the lower part of the spine. Lumbar spinal fusion surgery is also performed for patients who need relief from back pain, stabilization of the spine, and to restore a normal shape to the spine. The fusion part of the surgery relates to the growth of the new bones between the vertebral bodies.
Materials that are used for grafting are there to stimulate and promote this type of growth, which acts as a scaffolding across the disc space. There are a variety of growth-promoting materials for the bones to further accelerate the spinal fusion process.With all of the technology advances out there today, there are many products that can be used to decrease the need of using a patient’s own bone. Lumbar spinal fusion surgery helps to implant the hardware in the spine which in turn immobilizes the segments of the spine while the bones are fusing together, which could take up to six months to a year to occur.
Lumbar spinal fusion surgery can be performed for patients who are in need of back pain relief, stabilization of the spine, and to restore the spine back to its normal shape. Lumbar spinal fusion surgery can be performed once it is determined that the patients back pain is coming from the lumbar region of the back. The neurosurgeon may need to remove a large amount of bone in order to correctly decompress the nerve roots. Since this extensive amount of bone removal will decompress the nerves, the neurosurgeon will need to perform a spinal fusion to re-stabilize the spinal cord.
The procedure of how lumbar spinal fusion surgery works is the patient is first put to sleep and then be positioned in a way that the neurosurgeon deems best, so that he/she can reach between the vertebrae and perform the correct fusion procedure. There are many different interbody procedures and techniques that a neurosurgeon can use to achieving the best results for lumbar spinal fusion surgery. No matter what type of interbody spinal fusion is performed, there will need to be screws that will be used in the back of the spine to provide the firmness that the spine will need in order for the bones to fuse back together properly.
The postoperative care of lumbar spinal fusion surgery will usually consist of the patient being discharged anytime from one to four days following the lumbar spinal fusion surgery. The neurosurgeon will advise the patient to avoid bending, twisting, or lifting for several months after surgery and the patient will need to wear a back brace. There are a few potential risks of lumber spinal fusion surgery that patients will need to be aware of such as bleeding, infection, nerve injury, and the recurrence of another disc becoming herniated at the same level as before.
Spinal Cord Stimulator Implant Surgery
A spinal cord stimulator implant is considered to be a type of surgery or operation that could be beneficial for a patient, where a neurosurgeon will implant a spinal cord stimulator to help to decompress the nerves in the back. A spinal cord stimulator implant will help to send the electrical impulses to any area of the spinal cord that is causing the pain and will also help with the interference of the transmissions of the pain to the brain. A spinal cord stimulator implant will be able to block the brain’s ability to sense pain in the areas that are being stimulated, therefore relieving the patient’s pain without the unnecessary side effects that some medicines may cause.
A spinal cord stimulator implant has electrical impulses that can be rerouted to certain locations when the pain changes or improves. Before a neurosurgeon implants a spinal cord stimulator, the patient will need to participate in a trail stimulation group in order to see if the spinal cord stimulator implant will ultimately help their pain. If it works for the patient, then the neurosurgeon will put in a permanent spinal cord stimulator implant, where a battery pack will be implanted to help provide a charge to the spinal cord stimulator.
A spinal cord stimulator implant is best for patients who are encountering a significant amount of chronic lower extremity or back pain. There a few different ways that a neurosurgeon can implant a spinal cord stimulator into a patient. The first initial implantation of the spinal cord stimulator is usually done with the patient awake, so the neurosurgeon can determine if the spinal cord stimulator is working on the right spot of the spinal cord.
If after several days, the patient is achieving good pain relief, then the neurosurgeon can make the implant permanent for the patient. Patients of a spinal cord stimulator implant are usually discharged the day of or the following day of the surgery. The patient will be required to keep the incision very dry and clean. The risks for a spinal cord stimulator implant are fairly low, but there are some potential risks that a patient should be aware of and those include bleeding, infection, injured spinal cord, paralysis, and death.